1. The targeted bone (tibia or femur) is cut in a controlled fashion
Osteotomy surgery is a joint-preserving option for patients with early arthritis or joint damage isolated to one side of the knee.
At Dr. Samuel Duff’s orthopaedic clinic, we use carefully planned osteotomy techniques to realign the leg and relieve pressure on the worn part of the joint — without replacing it.
Osteotomy reshapes knee bones to shift weight away from damaged cartilage, relieving pain and delaying joint replacement.
Ideal for active patients under 55 with one-sided arthritis.
An osteotomy is a surgical procedure that involves reshaping or repositioning a bone to alter how forces travel through the joint. Around the knee, it’s commonly used to shift the body’s weight away from the damaged cartilage and onto healthier areas — delaying the need for joint replacement.
There are several types of osteotomies depending on alignment:
These procedures may also be combined with cartilage repair or meniscus surgery if needed.
Osteotomy is most appropriate for:
If joint degeneration becomes more widespread in future, an osteotomy does not prevent you from proceeding to a Total Knee Replacement later.
The main goal of osteotomy is to relieve pain and improve function by shifting weight-bearing to the healthier side of the knee.
Key benefits include:
This makes osteotomy an attractive option for young, active patients whose lifestyles are not compatible with prosthetic joint limitations.
As with all surgeries, osteotomy carries potential risks:
Dr. Duff will discuss these risks in detail and guide you through a recovery plan.
Dr. Duff uses digital planning and specialised imaging to calculate the exact angle needed for correction.
Movement of the knee typically begins within the first week, although partial weight-bearing is required initially to allow the osteotomy to heal properly.
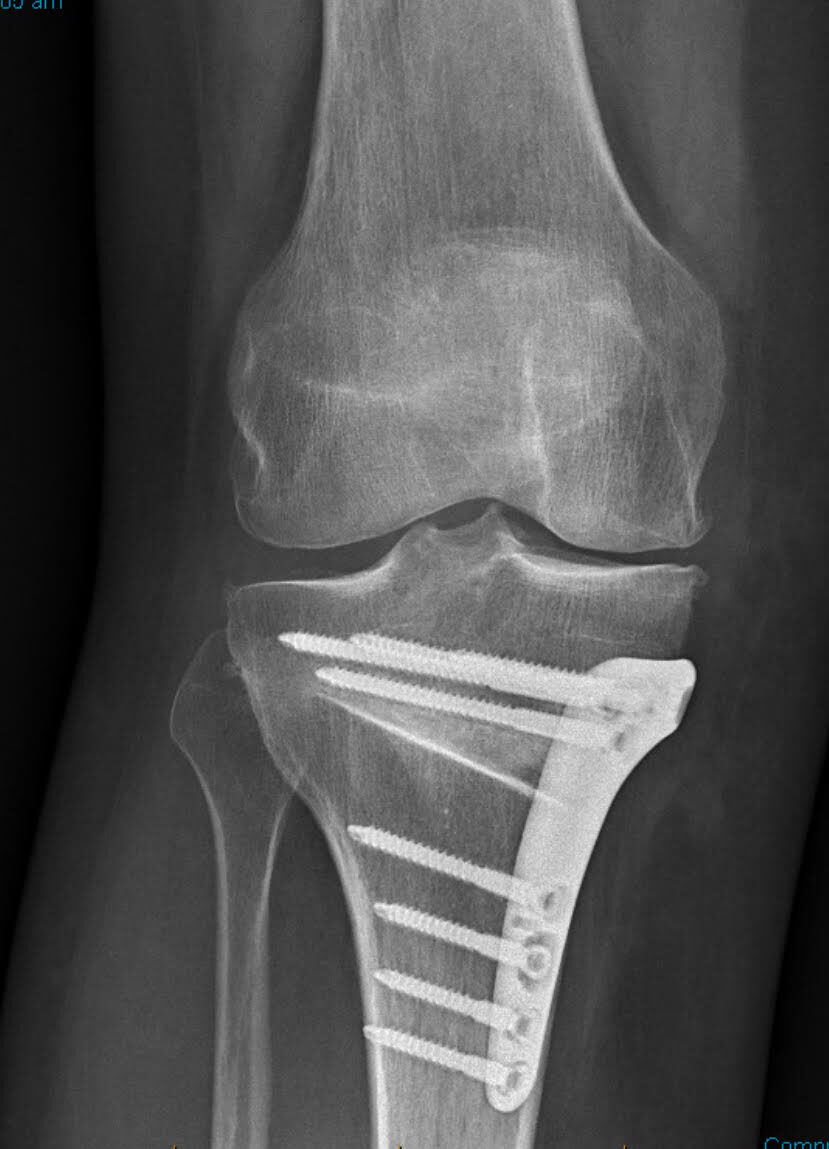
During the procedure:
1. The targeted bone (tibia or femur) is cut in a controlled fashion
2. The angle of the leg is opened or closed to change alignment
3. The new position is secured with a plate and screws
4. Over 6–10 weeks, the bone heals naturally into its new position
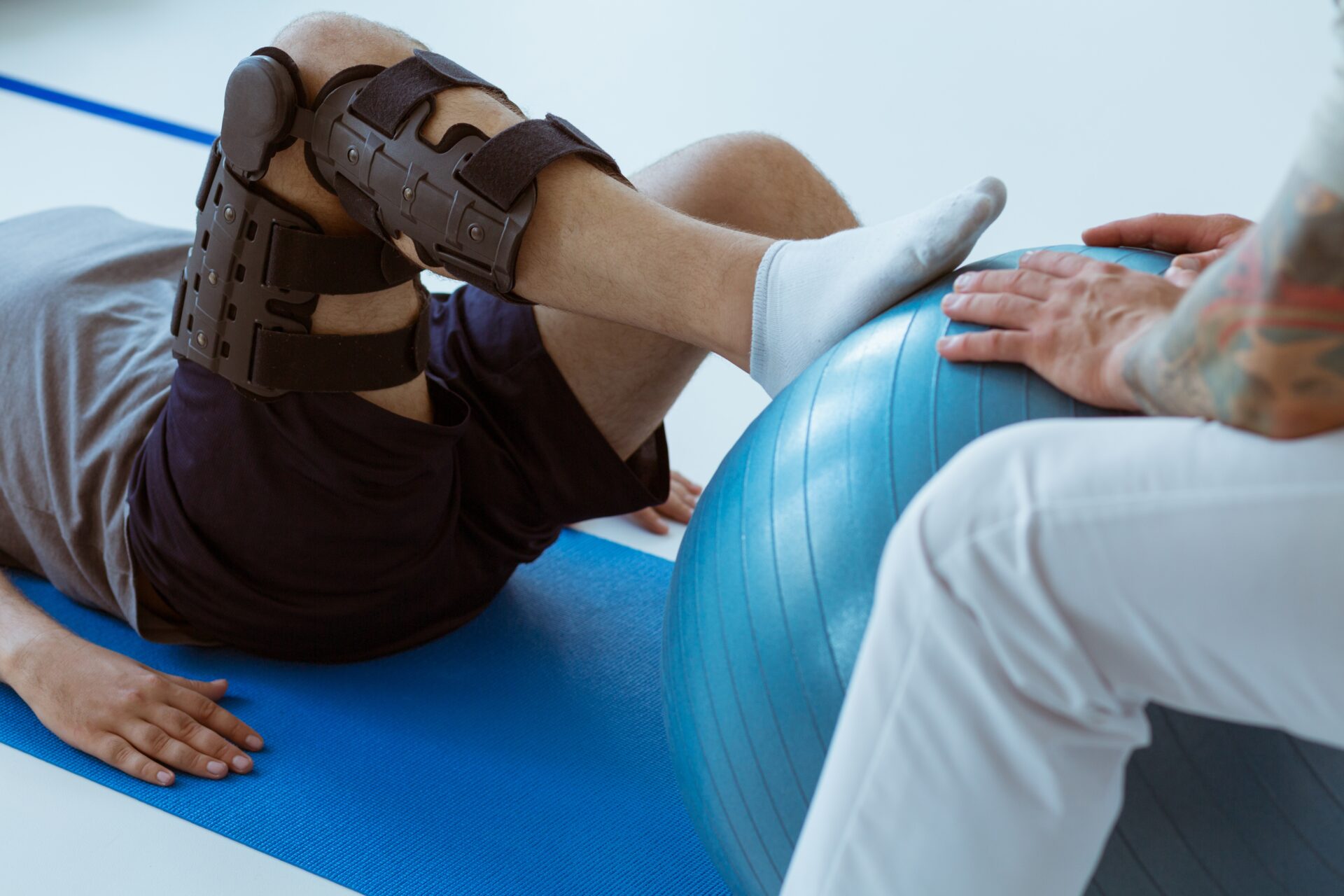

Most patients:
The bone typically heals by 10–12 weeks, after which weight-bearing and more intensive exercise can resume.
If you have early knee arthritis or pain localised to one side of the joint, osteotomy may offer long-term relief while preserving your natural knee.
Schedule a consultation with Dr. Samuel Duff to assess your options.